-
 Diagnosis of Peritonsillar Abscess—A Prospective Study Comparing Clinical with CT Findings in 133 Consecutive Patients
Diagnosis of Peritonsillar Abscess—A Prospective Study Comparing Clinical with CT Findings in 133 Consecutive Patients -
 The Dynamic Evolution of Eosinophilic Esophagitis
The Dynamic Evolution of Eosinophilic Esophagitis -
 Echocardiography with Strain Assessment in Psychiatric Diseases: A Narrative Review
Echocardiography with Strain Assessment in Psychiatric Diseases: A Narrative Review -
 How to Effectively Communicate Dismal Diagnoses in Dermatology and Venereology: From Skin Cancers to Sexually Transmitted Infections
How to Effectively Communicate Dismal Diagnoses in Dermatology and Venereology: From Skin Cancers to Sexually Transmitted Infections -
 Transforming Microbiological Diagnostics in Nosocomial Lower Respiratory Tract Infections: Innovations Shaping the Future
Transforming Microbiological Diagnostics in Nosocomial Lower Respiratory Tract Infections: Innovations Shaping the Future
Journal Description
Diagnostics
Diagnostics
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on medical diagnosis published semimonthly online by MDPI. The British Neuro-Oncology Society (BNOS), the International Society for Infectious Diseases in Obstetrics and Gynaecology (ISIDOG) and the Swiss Union of Laboratory Medicine (SULM) are affiliated with Diagnostics and their members receive a discount on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, Embase, Inspec, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Medicine, General and Internal) / CiteScore - Q2 (Internal Medicine)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 20.3 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2024).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Companion journals for Diagnostics include: LabMed and AI in Medicine.
Impact Factor:
3.0 (2023);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.1 (2023)
Latest Articles
Endoscopic Full Thickness Resection Device (FTRD®) for the Management of Gastrointestinal Lesions: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives
Diagnostics 2025, 15(7), 932; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070932 (registering DOI) - 4 Apr 2025
Abstract
Endoscopic full-thickness resection (EFTR) has emerged as a transformative technique for managing gastrointestinal (GI) lesions, previously deemed unsuitable for endoscopic removal. Unlike conventional endoscopic resection methods, such as endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD), EFTR enables en bloc excision of
[...] Read more.
Endoscopic full-thickness resection (EFTR) has emerged as a transformative technique for managing gastrointestinal (GI) lesions, previously deemed unsuitable for endoscopic removal. Unlike conventional endoscopic resection methods, such as endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD), EFTR enables en bloc excision of both intraluminal and subepithelial lesions by resecting all layers of the GI wall, followed by defect closure to prevent complications. The introduction of the full-thickness resection device (FTRD®) has significantly enhanced the feasibility and safety of EFTR, particularly in the colon and upper GI tract, with increasing adoption worldwide. This review provides a comprehensive analysis of FTRD®, focusing on its clinical applications, procedural methodology, and comparative efficacy against other endoscopic resection techniques. The indications and contraindications for EFTR are explored, highlighting its utility in treating non-lifting adenomas, subepithelial tumours, and T1 carcinomas without lymph node involvement. This review synthesizes current clinical data and FTRD® advantages. Despite its strengths, EFTR via FTRD® incorporates challenges such as limitations in lesion size, procedural complexity, and potential adverse events. Strategies for overcoming these challenges, including hybrid techniques and modifications in procedural approach, are examined. The review also emphasizes the need for further research to optimize surveillance strategies and determine the long-term clinical impact of EFTR in GI lesion management. By integrating recent evidence, this paper provides valuable insights into the evolving role of EFTR in therapeutic endoscopy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Diagnosis and Prognosis of Abdominal Diseases)
Open AccessArticle
Telomere Length and Genetic Variations in Acquired Pediatric Aplastic Anemia: A Flow-FISH Study in Korean Patients
by
Yuna Hong, Jong-Mi Lee, Chaeyeon Lee, Duyeon Na, Jin Jung, Ari Ahn, Jae Won Yoo, Jae Wook Lee, Nack-Gyun Chung, Myungshin Kim and Yonggoo Kim
Diagnostics 2025, 15(7), 931; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070931 (registering DOI) - 4 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: Aplastic anemia (AA) is a rare bone marrow failure syndrome characterized by notably short telomere length, which is associated with treatment responses. In this study, we measured telomere lengths in Korean pediatric AA patients using flow-fluorescence in situ hybridization (Flow-FISH) and
[...] Read more.
Background: Aplastic anemia (AA) is a rare bone marrow failure syndrome characterized by notably short telomere length, which is associated with treatment responses. In this study, we measured telomere lengths in Korean pediatric AA patients using flow-fluorescence in situ hybridization (Flow-FISH) and explored their shortening in relation to disease characteristics, genetic conditions and patient outcomes. Methods: We analyzed peripheral blood samples from 75 AA patients and 101 healthy controls. Telomere lengths were measured using Flow-FISH, and relative telomere length (RTL) and delta RTL assessments were conducted. Genetic evaluations included karyotyping, chromosome breakage tests and clinical exome sequencing (CES) to identify inherited bone marrow failure syndrome (IBMFS)-associated genetic variants. Results: Telomere lengths in AA patients were significantly lower than those of age-adjusted healthy controls. Patients receiving immunosuppressive therapy tended to have long telomeres, as indicated by high delta RTL values. Patients with genetic abnormalities, including karyotype abnormalities (n = 2) and genetic variants (n = 11) such as carrier genes of IBMFS or variants of unclear significance, showed significantly short telomere lengths. Conclusions: This study reinforces the importance of telomere length as a biomarker in acquired AA. Utilizing Flow-FISH, we were able to accurately measure telomere lengths and establish confidence in this method as an appropriate laboratory test. We found significant reduction in telomere lengths in AA patients, and importantly, longer telomeres were correlated with better outcomes in immunosuppressive therapy. Additionally, our genetic analysis underscored the relevance of variants in IBMFS-associated genes to the pathophysiology of short telomeres.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pathology and Molecular Diagnostics)
►▼
Show Figures
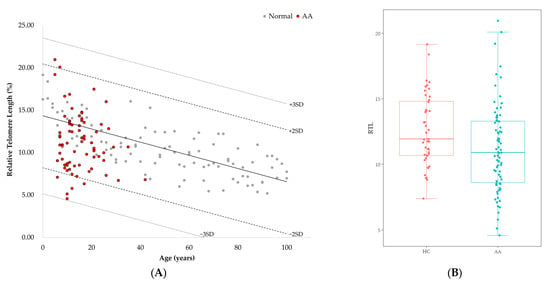
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Information Extraction from Lumbar Spine MRI Radiology Reports Using GPT4: Accuracy and Benchmarking Against Research-Grade Comprehensive Scoring
by
Katharina Ziegeler, Virginie Kreutzinger, Michelle W. Tong, Cynthia T. Chin, Emma Bahroos, Po-Hung Wu, Noah Bonnheim, Aaron J. Fields, Jeffrey C. Lotz, Thomas M. Link and Sharmila Majumdar
Diagnostics 2025, 15(7), 930; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070930 (registering DOI) - 4 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: This study aimed to create a pipeline for standardized data extraction from lumbar-spine MRI radiology reports using a large language model (LLM) and assess the agreement of the extracted data with research-grade semi-quantitative scoring. Methods: We included a subset of
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: This study aimed to create a pipeline for standardized data extraction from lumbar-spine MRI radiology reports using a large language model (LLM) and assess the agreement of the extracted data with research-grade semi-quantitative scoring. Methods: We included a subset of data from a multi-site NIH-funded cohort study of chronic low back pain (cLBP) participants. After initial prompt development, a secure application programming interface (API) deployment of OpenAIs GPT-4 was used to extract different classes of pathology from the clinical radiology report. Unsupervised UMAP and agglomerative clustering of the pathology terms’ embeddings provided insight into model comprehension for optimized prompt design. Model extraction was benchmarked against human extraction (gold standard) with F1 scores and false-positive and false-negative rates (FPR/FNR). Then, an expert MSK radiologist provided comprehensive research-grade scores of the images, and agreement with report-extracted data was calculated using Cohen’s kappa. Results: Data from 230 patients with cLBP were included (mean age 53.2 years, 54% women). The overall model performance for extracting data from clinical reports was excellent, with a mean F1 score of 0.96 across pathologies. The mean FPR was marginally higher than the FNR (5.1% vs. 3.0%). Agreement with comprehensive scoring was moderate (kappa 0.424), and the underreporting of lateral recess stenosis (FNR 63.6%) and overreporting of disc pathology (FPR 42.7%) were noted. Conclusions: LLMs can accurately extract highly detailed information on lumbar spine imaging pathologies from radiology reports. Moderate agreement between the LLM and comprehensive scores underscores the need for less subjective, machine-based data extraction from imaging.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue AI in Radiology and Nuclear Medicine: Challenges and Opportunities)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Distillation Approach to Transformer-Based Medical Image Classification with Limited Data
by
Aynur Sevinc, Murat Ucan and Buket Kaya
Diagnostics 2025, 15(7), 929; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070929 (registering DOI) - 4 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Although transformer-based deep learning architectures are preferred in many hybrid architectures due to their flexibility, they generally perform poorly on image classification tasks with small datasets. An important improvement in performance when transformer architectures work with limited data is the use
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Although transformer-based deep learning architectures are preferred in many hybrid architectures due to their flexibility, they generally perform poorly on image classification tasks with small datasets. An important improvement in performance when transformer architectures work with limited data is the use of distillation techniques. The impact of distillation techniques on classification accuracy in transformer-based models has not yet been extensively investigated. Methods: This study investigates the impact of distillation techniques on the classification performance of transformer-based deep learning architectures trained on limited data. We use transformer-based models ViTx32 and ViTx16 without distillation and DeiT and BeiT with distillation. A four-class dataset of brain MRI images is used for training and testing. Results: Our experiments show that the DeiT and BeiT architectures with distillation achieve performance gains of 2.2% and 1%, respectively, compared to ViTx16. A more detailed analysis shows that the distillation techniques improve the detection of non-patient individuals by about 4%. Our study also includes a detailed analysis of the training times for each architecture. Conclusions: The results of the experiments show that using distillation techniques in transformer-based deep learning models can significantly improve classification accuracy when working with limited data. Based on these findings, we recommend the use of transformer-based models with distillation, especially in medical applications and other areas where flexible models are developed with limited data.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue AI and Big Data in Healthcare)
►▼
Show Figures
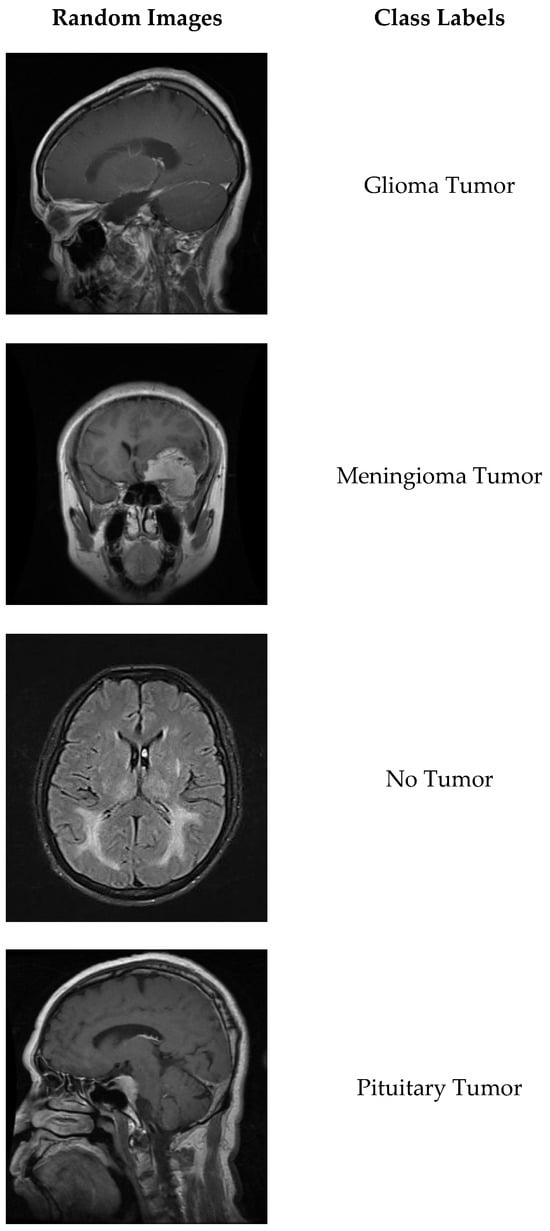
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Usefulness of the CDC/AAP and the EFP/AAP Criteria to Detect Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Subjects with Diabetes and Severe Periodontal Disease
by
Greicy C. Montenegro-González, Carlos Bea, F. Javier Ampudia-Blasco, Herminia González-Navarro, José T. Real, Maria Peñarrocha-Diago and Sergio Martínez-Hervás
Diagnostics 2025, 15(7), 928; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070928 (registering DOI) - 4 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease associated with many systemic disorders such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease. The aim was to evaluate the usefulness of the CDC/AAP and the EFP/AAP criteria to detect subclinical atherosclerosis in subjects with diabetes and severe periodontal
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease associated with many systemic disorders such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease. The aim was to evaluate the usefulness of the CDC/AAP and the EFP/AAP criteria to detect subclinical atherosclerosis in subjects with diabetes and severe periodontal disease. Methods: This was a cross-sectional study. Atheroma plaque was evaluated by high-resolution carotid and femoral ultrasonography. A dental examination protocol was implemented by a trained periodontist. A full-mouth periodontal clinical examination was carried out at six sites by automated computerized Florida Probe Periodontal Probing. Periodontal disease was defined by CDC/AAP and EFP/AAP criteria. Results: In total, 98 patients were included (60.2% women), of which 50% had diabetes. Subjects with diabetes showed a high prevalence of severe cases of periodontal disease. Both criteria were useful to detect the presence of atheroma plaque only in the presence of diabetes. However, the CDC/AAP criteria had higher correlation with atheroma plaques than EFP/AAP criteria (r = 0.522 vs. r = 0.369, p < 0.001). Conclusions: The CDC/AAP and the EFP/AAP criteria are a useful tool to identify subclinical atherosclerosis in subjects with severe periodontal disease and diabetes. These results show the potential role of the oral healthcare team in the dental office for the identification of subjects with diabetes at risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Periodontal Disease: Diagnosis and Management)
Open AccessArticle
Evaluating the Nuclear Reaction Optimization (NRO) Algorithm for Gene Selection in Cancer Classification
by
Shahad Alkamli and Hala Alshamlan
Diagnostics 2025, 15(7), 927; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070927 (registering DOI) - 3 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Cancer classification using microarray datasets presents a significant challenge due to their extremely high dimensionality. This complexity necessitates advanced optimization methods for effective gene selection. Methods: This study introduces and evaluates the Nuclear Reaction Optimization (NRO)—drawing inspiration from nuclear fission
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Cancer classification using microarray datasets presents a significant challenge due to their extremely high dimensionality. This complexity necessitates advanced optimization methods for effective gene selection. Methods: This study introduces and evaluates the Nuclear Reaction Optimization (NRO)—drawing inspiration from nuclear fission and fusion—for identifying informative gene subsets in six benchmark cancer microarray datasets. Employed as a standalone approach without prior dimensionality reduction, NRO was assessed using both Support Vector Machine (SVM) and k-Nearest Neighbors (k-NN). Leave-One-Out Cross-Validation (LOOCV) was used to rigorously evaluate classification accuracy and the relevance of the selected genes. Results: Experimental results show that NRO achieved high classification accuracy, particularly when used with SVM. In select datasets, it outperformed several state-of-the-art optimization algorithms. However, due to the absence of additional dimensionality reduction techniques, the number of selected genes remains relatively high. Comparative analysis with Harris Hawks Optimization (HHO), Artificial Bee Colony (ABC), Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), and Firefly Algorithm (FFA) shows that while NRO delivers competitive performance, it does not consistently outperform all methods across datasets. Conclusions: The study concludes that NRO is a promising gene selection approach, particularly effective in certain datasets, and suggests that future work should explore hybrid models and feature reduction techniques to further enhance its accuracy and efficiency.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advancing Clinical Diagnosis with Artificial Intelligence: Applications, Challenges, and Future Directions)
►▼
Show Figures
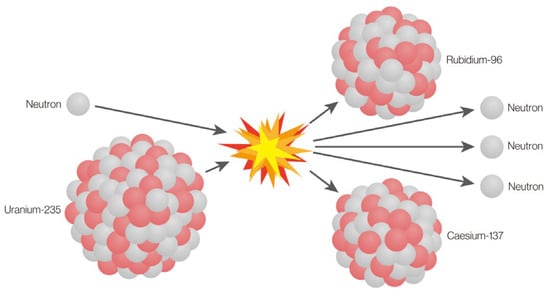
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Application and Validity of a New Composite Radiographic Index for Patients with Osteonecrosis of the Jaws
by
Zafeiroula Yfanti, Sotirios Tetradis, Nikolaos G. Nikitakis, Konstantina Eleni Alexiou, Emmanouil Vardas, Christos Angelopoulos and Kostas Tsiklakis
Diagnostics 2025, 15(7), 926; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070926 (registering DOI) - 3 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: This study aims to determine the validity of a recently developed and published index (the modified Composite Radiographic Index—CRIm) as an indicator of disease gravity and progression in the CBCT scans of patients with medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ) and
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: This study aims to determine the validity of a recently developed and published index (the modified Composite Radiographic Index—CRIm) as an indicator of disease gravity and progression in the CBCT scans of patients with medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ) and to detect possible correlations between the radiologic findings and clinical staging of the disease. Methods: This study included 43 MRONJ patients with CBCT scans from the School of Dentistry of National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, approved by the Research Ethics Committee. Clinical staging (0–3) was provided based on AAOMS 2022 guidelines. A total of 52 CBCT scans were analyzed, with maxillae and mandibles evaluated separately when both were involved. Two independent observers assessed eight radiologic features, including lytic changes, sclerosis, periosteal reaction, sequestration, non-healing extraction sockets, and other findings (sinus involvement, inferior alveolar canal involvement, and jaw fracture). The CRIm was applied to quantify osseous changes, scoring each feature (0 (absent), 1 (localized/single), 2 (extensive/multiple)), yielding a range of 0–12. For the statistical analysis, Fisher’s exact test and Spearman’s correlation coefficient were used. Results: Clinical Stage 1 consisted of 19 jaws, Stage 2 consisted of 16 jaws, and Stage 3 consisted of 17 jaws. No affected jaws were recorded with Stage 0. A statistically significant correlation between the clinical stage and lytic changes, sequestration, and inferior alveolar canal involvement was found (p-value < 0.05). Extensive lytic changes, sclerosis, sequestration, periosteal bone formation, and inferior alveolar canal involvement were mostly observed in clinical Stage 3. Furthermore, a statistically significant correlation between clinical stage and CRIm classification was found (rho = 0.446; p-value < 0.001). Conclusions: The CRIm tends to increase as the clinical stages of MRONJ advance, suggesting a correlation between them.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Medical Imaging and Theranostics)
►▼
Show Figures
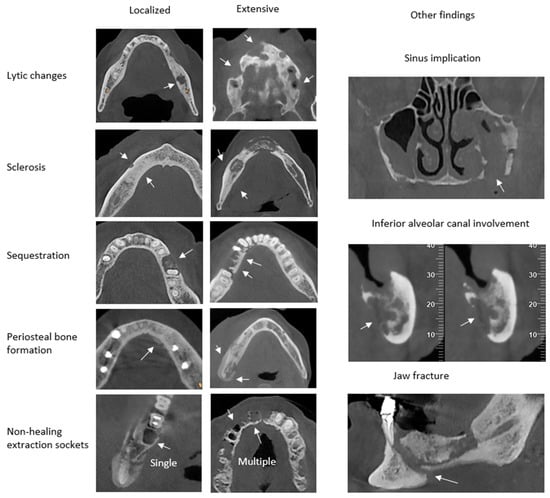
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
The Anatomy of the Stylohyoid Chain: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis
by
George Triantafyllou, Ioannis Paschopoulos, Fabrice Duparc, George Tsakotos, Panagiotis Papadopoulos-Manolarakis and Maria Piagkou
Diagnostics 2025, 15(7), 925; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070925 - 3 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: The temporal bone’s styloid process (SP) is an important structure that extends from the skull base to the parapharyngeal space. The stylohyoid ligament (SHL) attaches it to the hyoid bone. The SP and SHL are considered the stylohyoid chain (SHC) components.
[...] Read more.
Background: The temporal bone’s styloid process (SP) is an important structure that extends from the skull base to the parapharyngeal space. The stylohyoid ligament (SHL) attaches it to the hyoid bone. The SP and SHL are considered the stylohyoid chain (SHC) components. The SP’s close relationship with vital head and neck structures has important clinical implications. Specifically, SP and SHC variants are linked with clinical conditions. Therefore, adequate knowledge of these variations is of paramount importance. Methods: Using the latest guidelines, a systematic literature review was performed in four online databases (PubMed, Google Scholar, Scopus, and Web of Science) to identify studies referring to the SP’s typical anatomy and possible SHC morphological variants. The meta-analysis was conducted using R programming software to calculate the prevalence of typical anatomy and possible variants and the pooled mean length of the SP. Results: A total of 104 studies were included, with a total sample of 136,010 heminecks. The typical SP (under 30 mm) was estimated to have a pooled prevalence of 74.97%. SP elongation was observed in 25.03%. The subgroup analysis identified significant differences based on the study type, with computed tomography (CT) studies having the highest pooled prevalence. The SP length was calculated to have a pooled mean of 28.91 mm. For SHC ossification, the pseudo-articulated type was identified to have a pooled prevalence of 4.39%, and that of the segmented type was detected to be 3.89%. The geographical distribution and study type affected the estimated pooled prevalence. Conclusions: The current evidence-based systematic review with meta-analysis investigated the SHC’s typical anatomy and possible variants. The elongated SP pooled prevalence of 25.03% indicates that it is not a rare variant, and CT is the optimal method to investigate such a variant. These details demonstrated by the current meta-analysis could be of importance for clinicians.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Clinical Anatomy and Diagnosis in 2025)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
An Incidental Finding of Appendiceal Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor with Abundant Skeinoid Fibers: A Rare Case Report with Insights from a Comprehensive Literature Review
by
Yu Liu, Yaomin Chen, Asra Feroze and Zhiyan Fu
Diagnostics 2025, 15(7), 924; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070924 - 3 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background and Clinical Significance: Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are the most common mesenchymal tumors of the gastrointestinal tract but are exceedingly rare in the appendix, with only 20 cases reported in the literature. Due to their rarity, clinical behavior, histopathologic features, and management
[...] Read more.
Background and Clinical Significance: Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are the most common mesenchymal tumors of the gastrointestinal tract but are exceedingly rare in the appendix, with only 20 cases reported in the literature. Due to their rarity, clinical behavior, histopathologic features, and management of appendiceal GISTs remain poorly understood. Case Presentation: We present the case of a 74-year-old man who underwent a right hemicolectomy for colonic adenocarcinoma, during which an incidental 1.2 cm appendiceal GIST was discovered. Histopathological examination revealed spindle cell morphology with abundant skeinoid fibers (SF), minimal mitotic activity (<1/50 HPF), and no nuclear atypia. Immunohistochemical staining confirmed positivity for CD117, DOG1, and CD34. The tumor was classified as low risk based on its size and mitotic count, and the patient remained recurrence-free at a 4-month follow-up. Conclusions: Our case expands the limited literature on appendiceal GISTs by demonstrating their histopathological and immunohistochemical features, favorable prognostic outcomes, and potential for incidental detection during surgeries for unrelated conditions. However, additional studies are needed to further elucidate their molecular characteristics and overall clinical behavior.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pathology and Molecular Diagnostics)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Analytical Validation of MyProstateScore 2.0
by
Jacob I. Meyers, Tabea M. Schatz, Cameron J. Seitz, Rachel Botbyl, Bradley S. Moore, Bill G. Crafts, John R. Kitchen and Spencer Heaton
Diagnostics 2025, 15(7), 923; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070923 - 3 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Prostate cancer (PCa) is a leading cause of cancer-related deaths among men, with early detection playing a crucial role in improving outcomes. MyProstateScore 2.0 (MPS2), a novel urinary biomarker test, predicts clinically significant PCa to reduce invasive biopsy procedures. This study
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Prostate cancer (PCa) is a leading cause of cancer-related deaths among men, with early detection playing a crucial role in improving outcomes. MyProstateScore 2.0 (MPS2), a novel urinary biomarker test, predicts clinically significant PCa to reduce invasive biopsy procedures. This study evaluates the analytical performance of MPS2 using both a post-digital rectal exam (DRE) and non-DRE urine samples. Methods: We assessed the reproducibility, precision, and detection limits of the eighteen MPS2 analytes. Analytical parameters including the linear range, upper and lower limits of quantification (ULOQ and LLOQ), and interference from substances commonly present in urine were evaluated. The reproducibility of the MPS2 scores was evaluated across post-DRE and non-DRE clinical urine samples. Results: MPS2 analytes demonstrated high linearity (R2 ≥ 0.975) across defined quantification ranges, with PCR efficiencies of 97–105%. The limits of detection (LOD) ranged from 40 to 160 copies/reaction, while the ULOQ was determined to be 106–107 copies/reaction for each analyte. Precision studies showed intra-run, inter-run, and inter-instrument standard deviations ≤0.5 Crt. Among the 12 potential interfering substances, only whole blood affected the performance of MPS2. The reproducibility of the MPS2 scores was consistent across post-DRE and non-DRE urine samples, meeting the acceptance criteria. Conclusions: The analytical validation confirms that MPS2 is robust and reliable in detecting biomarkers for clinically significant PCa. These findings, coupled with previous clinical validations, support the clinical use of MPS2 as a non-invasive diagnostic tool.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Clinical Laboratory Medicine)
►▼
Show Figures
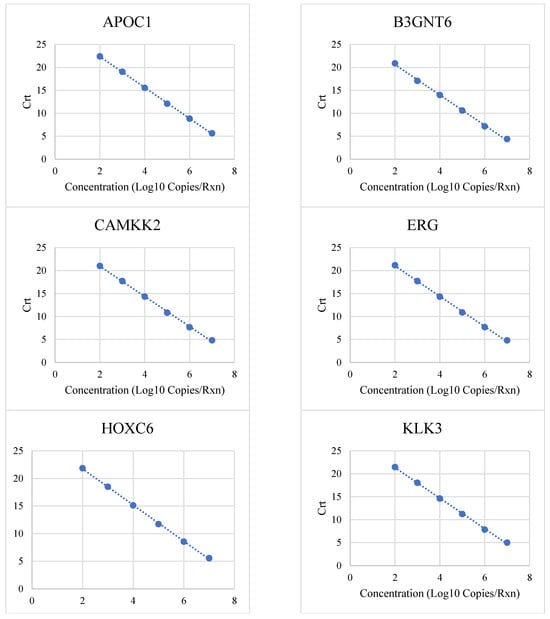
Figure 1
Open AccessBrief Report
Identification of Coronary Morphological Damage in Patients with Chronic Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases
by
Elena Heras-Recuero, Juan Antonio Martínez-López, Macarena Garbayo-Bugeda, Álvaro Castrillo-Capilla, Teresa Blázquez-Sánchez, Arantxa Torres-Roselló, Antia García-Fernández, Javier Llorca, Raquel Largo, Juan Antonio Franco-Peláez, José Tuñón and Miguel Ángel González-Gay
Diagnostics 2025, 15(7), 922; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070922 - 2 Apr 2025
Abstract
Objective: Patients with chronic inflammatory rheumatic diseases (CIRDs) have a higher incidence of coronary artery disease (CAD) due to accelerated atherogenesis. This study aimed to assess the extent and location of CAD lesions in CIRD patients compared to non-CIRD patients. Methods: A retrospective
[...] Read more.
Objective: Patients with chronic inflammatory rheumatic diseases (CIRDs) have a higher incidence of coronary artery disease (CAD) due to accelerated atherogenesis. This study aimed to assess the extent and location of CAD lesions in CIRD patients compared to non-CIRD patients. Methods: A retrospective study was conducted on CIRD patients (rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and psoriatic arthritis) who underwent coronary angiography at Hospital Fundación Jiménez Díaz (Madrid, Spain) between 2018 and 2022. For each CIRD patient, at least two frequency-matched controls were selected based on sex, age (±2 years), diabetic status, and clinical indication for coronary angiography. The indications for coronary angiography in both groups were chronic coronary syndrome and acute coronary syndrome with or without ST elevation. Results: A total of 66 CIRD patients were included, with 42 (63.6%) women, and a median age of 66.6 years (range: 58.3–75.2). Compared to the controls, CIRD patients had a higher number of affected coronary arteries (2.03 vs. 1.56, p = 0.03). The mid-anterior descending artery and the right posterior descending artery were more frequently involved in CIRD patients than in controls (odds ratio [OR] of 2.45 and 3.53, respectively, p ≤ 0.02 for both comparisons). The frequency of coronary calcification was higher in CIRD patients, though the difference did not reach statistical significance (5 of 66 in CIRD patients vs. 3 of 140 in non-CIRD controls, OR of 3.74, p = 0.06). Revascularization was more commonly performed in patients with CIRD (50 of 66 vs. 85 of 140 in those without CIRD (OR: 2.02 [95% CI: 1.01–4.18]; p = 0.03). Conclusions: Patients with CIRD exhibit more extensive CAD, with a higher propensity for involvement inthe mid-anterior descending and right posterior descending arteries compared to patients without CIRD. These findings highlight the need for closer cardiovascular monitoring and early risk stratification in CIRD patients to improve the detection and management of CAD.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Diagnosis, Prognosis and Management of Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Rheumatic Conditions)
►▼
Show Figures
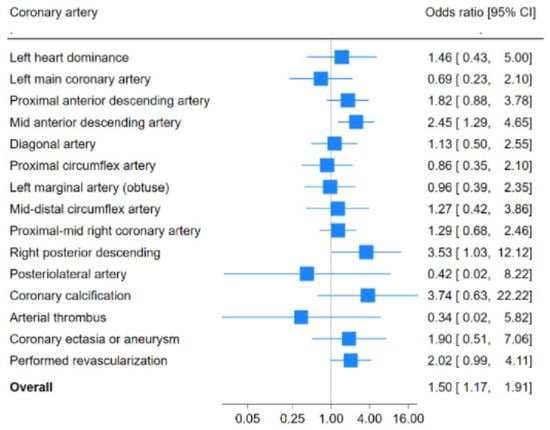
Figure 1
Open AccessGuidelines
Best Practices for the Use of High-Frequency Ultrasound to Guide Esthetic Filler Injections—Part 3: Lower Third of the Face
by
Roberta Vasconcelos-Berg, Stella Desyatnikova, Paula Bonavia, Alexander Navarini, Maria Cristina Chammas and Rosa Sigrist
Diagnostics 2025, 15(7), 921; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070921 - 2 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: The lower third of the face plays a crucial role in overall facial harmony, and age-related volume loss in areas such as the pre-jowl region, labiomental folds, and lips can significantly impact esthetic appearance. High-resolution ultrasound is helpful for identifying key structures,
[...] Read more.
Background: The lower third of the face plays a crucial role in overall facial harmony, and age-related volume loss in areas such as the pre-jowl region, labiomental folds, and lips can significantly impact esthetic appearance. High-resolution ultrasound is helpful for identifying key structures, such as the facial artery, parotid gland, and masseter muscle, which are critical to avoid during filler injections. Objectives: This article, the final installment in a three-part series on ultrasound-guided facial injections, provides an in-depth analysis of the sonographic anatomy of the lower face, including the mandibular, marionette, and chin regions. Methods: This article outlines step-by-step techniques for ultrasound-guided filler procedures, with a focus on the importance of pre- and intra-procedural scanning to ensure safe and accurate filler placement. Results: By employing techniques like “scan before injecting” and “scan while injecting”, injectors aim to reduce risks such as vascular occlusion, muscle injection, and skin necrosis. Discussion: The use of ultrasound guidance in these regions enhances both esthetic outcomes and patient safety, providing optimal results while minimizing complications. With continued advancements, ultrasound-guided injections will become increasingly precise, enabling more targeted and safer treatments in the lower face.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Ultrasound in the Diagnosis and Management of Skin Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
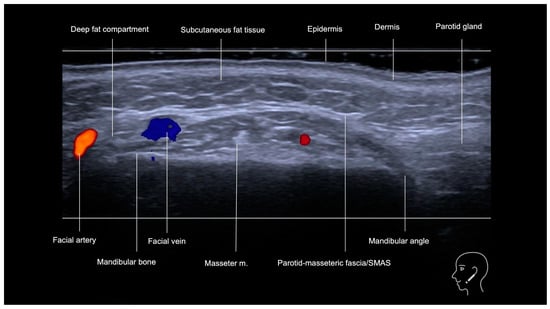
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Federated Learning-Based CNN Models for Orthodontic Skeletal Classification and Diagnosis
by
Demet Süer Tümen and Mehmet Nergiz
Diagnostics 2025, 15(7), 920; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070920 - 2 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Accurate skeletal classification is essential for orthodontic diagnosis. This study evaluates the effectiveness of federated convolutional neural network (CNN) models for skeletal classification using cephalometric images from the ISBI and Dicle datasets. This research aims to evaluate the effectiveness of federated learning
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Accurate skeletal classification is essential for orthodontic diagnosis. This study evaluates the effectiveness of federated convolutional neural network (CNN) models for skeletal classification using cephalometric images from the ISBI and Dicle datasets. This research aims to evaluate the effectiveness of federated learning (FL) for orthodontic skeletal classification by comparing its performance against centralized learning (CL) and local learning (LL). The objective is to determine whether FL can achieve competitive performance while preserving data privacy and enabling collaborative model training across multiple institutions. Methods: The DenseNet121 model and its augmented versions, incorporating channel attention, spatial attention, squeeze and excitation, and spatial pyramid pooling blocks, are proposed and adapted for the study. Models are evaluated on the ISBI and Dicle datasets using accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity metrics, with performance gains benchmarked across CL, LL, and FL frameworks. Results: Accuracy improvements exceed 26% compared to the baseline model on FL framework. The DenseNet121_SA model, augmented with spatial pyramid pooling blocks, achieves a 20.86% performance gain over LL settings on the ISBI dataset. Similarly, the DenseNet121_SA model, augmented with spatial attention, and DenseNet121_SA_SE model, augmented with spatial attention and squeeze and excitation, obtain 16.58% and 15.22% by not sacrificing performance loss with respect to CL. The inclusion of the Dicle dataset provides additional validation for the models. Conclusions: Federated CNN models exhibit significant promise for orthodontic skeletal classification. These models demonstrate the potential of FL to enhance collaborative model training while preserving data privacy. This approach represents a step forward in leveraging precise orthodontic diagnostics technology by enabling a data-secure collaborative artificial intelligence among various orthodontic clinics.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Artificial Intelligence in the Diagnostics of Dental Diseases, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Ultrasound of Bile Ducts—An Update on Measurements, Reference Values, and Their Influencing Factors: A Scoping Review
by
Claudia Lucius, Anja Flückiger, Jennifer Meier, Kathleen Möller, Christian Jenssen, Barbara Braden, Michael Kallenbach, Benjamin Misselwitz, Christian Nolsøe, Michael Sienz, Constantinos Zervides and Christoph Frank Dietrich
Diagnostics 2025, 15(7), 919; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070919 - 2 Apr 2025
Abstract
Objective: To provide an overview of the technique and normal values of ultrasound studies of the bile system based on the published literature. Methods: A literature search for ultrasound studies with measurements of the bile ducts in healthy subjects was performed. Relevant data
[...] Read more.
Objective: To provide an overview of the technique and normal values of ultrasound studies of the bile system based on the published literature. Methods: A literature search for ultrasound studies with measurements of the bile ducts in healthy subjects was performed. Relevant data published between 1975 and end of 2024 were extracted, discussed, and complemented with the own experiences of the authors. The clinical implications are presented and discussed. Results: For the diameter of the common bile duct, reference values between 5 and 9 mm have been published. The main influencing factors are age and history of cholecystectomy, and other factors to be considered are discussed here. The cut-off for the common bile duct wall is set at 1.5 mm. The literature on measurements of intrahepatic bile ducts is scarce. A diameter of <2–3 mm can be considered normal. The method of ultrasound examination is presented here, as well as a comparison with other imaging methods and their clinical implications. Discussion: Standardized measurement techniques and normal values in the context of influencing factors are crucial for the ultrasound examination of the bile system.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Imaging Diagnosis in Abdomen, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Phenotypes and Genotypes of Children with Vitamin D-Dependent Rickets Type 1A: A Single Tertiary Pediatric Center in Vietnam
by
Thi Anh Thuong Tran, Tran Minh Dien, Ngoc Lan Nguyen, Khanh Ngoc Nguyen, Thi Bich Ngoc Can, Bui Phuong Thao, Nguyen Thi Thuy Hong, Van Khanh Tran, Thinh Huy Tran, Ngo Xuan Khoa, Nguyen Thi Kim Lien, Nguyen Thien Tao, Huy Hoang Nguyen and Chi Dung Vu
Diagnostics 2025, 15(7), 918; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070918 - 2 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: Vitamin D-dependent rickets type 1A (VDDR1A) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in the CYP27B1 gene, leading to a deficiency in active vitamin D (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D). This study examines the genotypic and phenotypic characteristics of VDDR1A in Vietnamese
[...] Read more.
Background: Vitamin D-dependent rickets type 1A (VDDR1A) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in the CYP27B1 gene, leading to a deficiency in active vitamin D (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D). This study examines the genotypic and phenotypic characteristics of VDDR1A in Vietnamese children. Patients and Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on 19 Vietnamese children diagnosed with VDDR1A. Clinical, radiological, biochemical, and molecular data were collected. Rickets Severity Scores (RSSs), biochemical parameters, and height standard deviation scores (HtSDSs) were used to assess the severity of the condition. Results: The study included 19 children from 17 families (ten males and nine females). The median age of rickets diagnosis was 19.2 months, while with VDDR1A, the median time of diagnosis was 7.5 months. Common symptoms among the children included thickened wrists and ankles (19/19), genu varum or genu valgum (18/19), failure to thrive (18/19), rachitic rosary (12/19), and delayed walking (11/19). The radiographic features showed that all children had cupping, splaying, and fraying, twelve children had rachitic rosary, and six exhibited pseudofractures. The biochemical findings showed severe hypocalcemia, normal or mildly low serum phosphate, elevated alkaline phosphatase and parathyroid hormone levels, and normal serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels. Genetic analysis identified biallelic CYP27B1 variants, including one known pathogenic frameshift mutation, c.1319_1325dup p.(Phe443Profs*24), one novel likely pathogenic missense variant, c.616C>T p.(Arg206Cys), and one novel pathogenic frameshift mutation, c.96_97del p.(Ala33Thrfs*299). The c.1319_1325dup p.(Phe443Profs*24) variant was the most common, present in 18 out of 19 children. Conclusions: The children with VDDR1A in this study presented with growth failure and skeletal deformities. Key findings included severe hypocalcemia, elevated alkaline phosphatase and parathyroid hormone levels, normal or elevated 25(OH)D, and high RSSs. Predominant frameshift mutations in CYP27B1, especially c.1319_1325dup, highlighted the importance of early genetic diagnosis for optimal management. Additionally, two novel CYP27B1 variants were identified, expanding the known mutation spectrum of VDDR1A.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Diagnosis and Management of Metabolic Bone Diseases: 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
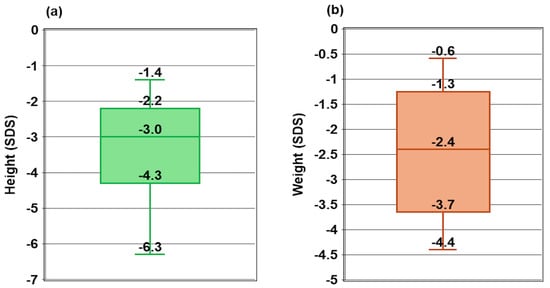
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Surgical Management of Sacral Bone Tumors: A Retrospective Analysis of Outcomes, Complications, and Survival
by
Chiara Cini, Emanuela Asunis, Cristiana Griffoni, Gisberto Evangelisti, Giuseppe Tedesco, Riccardo Ghermandi, Marco Girolami, Valerio Pipola, Silvia Terzi, Giovanni Barbanti Brodano, Stefano Bandiera, Stefano Boriani and Alessandro Gasbarrini
Diagnostics 2025, 15(7), 917; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070917 - 2 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: Primary malignant bone tumors are exceedingly rare, with an incidence of 0.5 to 1 per million, and sacral localization is even more uncommon, representing only 1–3.5% of these tumors. These malignancies are often diagnosed late due to their asymptomatic nature until
[...] Read more.
Background: Primary malignant bone tumors are exceedingly rare, with an incidence of 0.5 to 1 per million, and sacral localization is even more uncommon, representing only 1–3.5% of these tumors. These malignancies are often diagnosed late due to their asymptomatic nature until they present as large, advanced intrapelvic tumors. Management is complicated by the need for precise surgical intervention and the consideration of adjuvant therapies based on tumor histology and patient factors. Methods: We conducted a single-center, retrospective analysis of patients who underwent complete, partial, or hemisacrectomy for primary malignant bone tumors or recurrent sacral metastases. Excluded were patients with metastatic disease not necessitating sacrectomy. Data collected included demographics, clinical characteristics, tumor types, resection status, adjuvant therapies, recurrence, metastasis, and complications. Surgical approaches were categorized as posterior, anterior, or combined anterior–posterior. The primary outcomes were overall survival and disease-free survival, while the secondary outcomes focused on complication rates and functional outcomes. Results: The study included 19 patients (7 females, 12 males) with a mean age of 48.9 years at the time of surgery. Primary malignancies were present in 90% of patients. Surgical approaches varied: 20% underwent double access and 5% anterior access only, and the remainder had posterior approaches. High partial sacrectomy (above S3) was performed in 20%, while low sacrectomy (at or below S3) was performed in 80%. Complete resection with clean margins (R0) was achieved in 65% of cases, while 35% had R1 resections with microscopic tumor remnants. Root resection was necessary in 25% of patients. Local recurrence occurred in 25% of patients, with two requiring reoperation and neurological sacrifice. Distant metastases were observed in 20% of cases. Postoperative complications affected 60% of patients. The most common issues were surgical wound dehiscence with delayed healing (35%) and visceral changes affecting the bowel and urination (25%). No mechanical complications were reported. Conclusions: Sacrectomy remains a challenging procedure with substantial morbidity and variability in outcomes. The choice of surgical approach—posterior, anterior, or combined—depends on tumor location and extent. While posterior-only approaches are often preferred for lower sacral lesions, combined approaches may be necessary for more extensive tumors. Survival and disease-free survival rates are influenced by resection margins and the biological behavior of the tumor. Wide-margin resections (R0) are associated with lower local recurrence rates but do not eliminate the risk of distant metastases.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Diagnosis and Management of Soft Tissue and Bone Tumors)
►▼
Show Figures
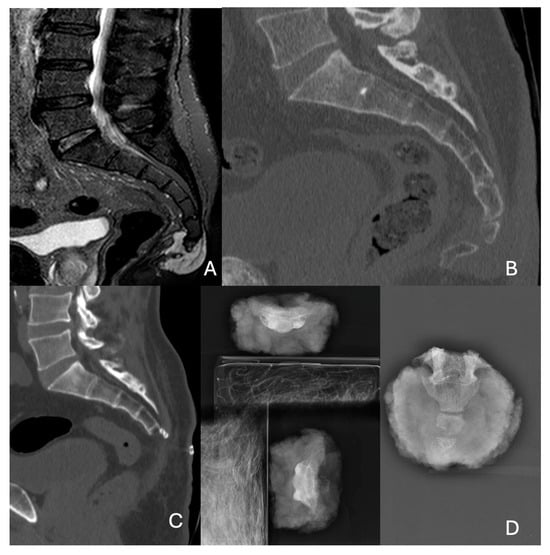
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Identification of Eye Diseases Through Deep Learning
by
Elena Acevedo, Dinora Orantes, Marco Acevedo and Ricardo Carreño
Diagnostics 2025, 15(7), 916; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070916 - 2 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: Ocular diseases have been a severe problem worldwide, specifically in underdeveloped countries that do not have enough technology or economy to treat them. It would be beneficial to have software with low installation complexity and ease of use, allowing high efficacy
[...] Read more.
Background: Ocular diseases have been a severe problem worldwide, specifically in underdeveloped countries that do not have enough technology or economy to treat them. It would be beneficial to have software with low installation complexity and ease of use, allowing high efficacy in diagnosing eye diseases. This study aims to design and implement an algorithm based on deep learning to classify ocular diseases with high precision. Methods: This work describes digital image processing techniques for the easier handling of eye images; in particular, blur filters were used. The Canny filter was also applied to obtain the edges that allow the difference between the analyzed diseases. Once the images were pre-processed, a convolutional neural network of our own design was applied to perform the classification task. The validation algorithm used in this work was the hold-out algorithm (80–20). The metrics used to evaluate our proposal were the confusion matrix, accuracy, recall precision, and F1-score. Results: The dataset has five classes, namely, normal, cataract, diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, and other retina diseases. The network architecture consists of 11 layers, including three convolutional layers, three max pooling layers, one batch normalization layer, one flattening layer, two hidden layers, and one output layer. This model resulted in 97% efficiency across all metrics. Conclusions: With the individual analysis of each metric, it can be observed that the proposed algorithm is capable of differentiating, first, images of healthy eyes from diseased ones and, second, adequately classifying eye diseases.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Updates on the Diagnosis and Management of Retinal Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
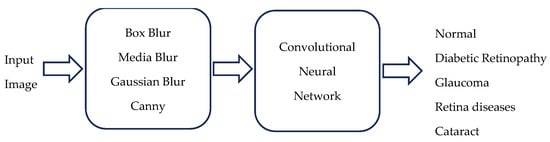
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Sex Bias in Frailty Screening: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of PRISMA-7 and the Clinical Frailty Scale in Primary Care
by
Christian J. Wiedermann, Verena Barbieri, Dietmar Ausserhofer, Adolf Engl, Giuliano Piccoliori and Angelika Mahlknecht
Diagnostics 2025, 15(7), 915; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070915 - 2 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Frailty screening is essential in primary care for the early identification of vulnerable older adults. PRISMA-7 is a widely used screening tool, but Item 2 (“Are you male?”) introduces potential sex bias and overestimates frailty in men. PRISMA-6, a modified version
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Frailty screening is essential in primary care for the early identification of vulnerable older adults. PRISMA-7 is a widely used screening tool, but Item 2 (“Are you male?”) introduces potential sex bias and overestimates frailty in men. PRISMA-6, a modified version that excludes Item 2, might provide a more equitable alternative. This study evaluates PRISMA-6’s alignment with the Clinical Frailty Scale (CFS) and its impact on sex-specific frailty classification. Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted in 142 general practices across South Tyrol, including 9190 general practice patients aged ≥75 years. Frailty was assessed using PRISMA-7, PRISMA-6, and the CFS. Correlations between tools were calculated using Kendall’s Tau-b, whereas Fisher’s z-test was used to compare differences in alignment. The frailty prevalence and odds ratios were stratified according to sex and age. Results: PRISMA-6 showed a stronger correlation with the CFS (τ = 0.492) than PRISMA-7 (τ = 0.308, z = −10.2, p < 0.001). This effect was pronounced in men (z = −9.8, p < 0.001), whereas no difference was observed in women (z = 0.00, p = 1.000). PRISMA-6 reduced the frailty detection rate in men and was more closely aligned with the CFS. Conclusions: PRISMA-6 demonstrated improved alignment with the CFS and reduced sex bias compared to PRISMA-7. However, its use as a screening tool for men requires prospective validation in diverse settings. PRISMA-6 shows promise as a reliable and equitable frailty screening tool and should be considered for use in future studies, particularly in primary care settings, while awaiting further prospective validation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Risk Factors for Frailty in Older Adults)
►▼
Show Figures
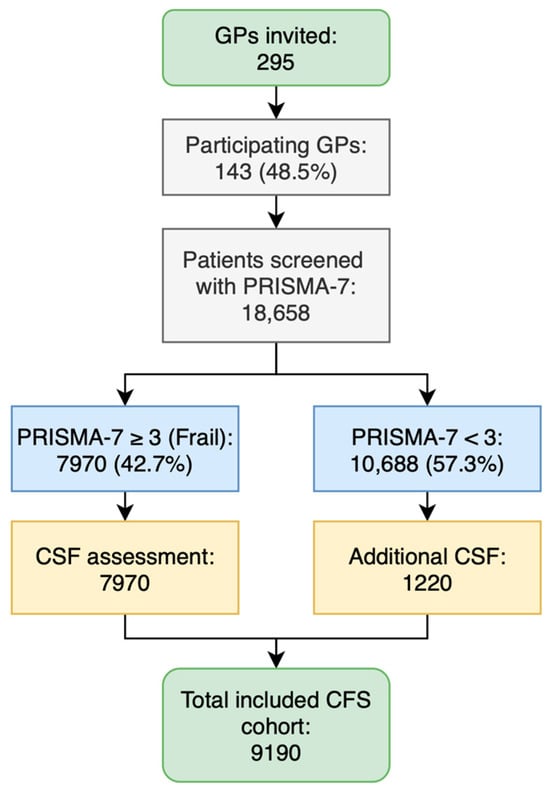
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Mesopancreas—Anatomical Insights and Its Implications for Diagnosis and Clinical and Surgical Practice
by
Florin-Mihail Filipoiu, Georgian-Theodor Badea, Mihaly Enyedi, Ștefan Oprea, Zoran-Florin Filipoiu and Daniela-Elena Gheoca Mutu
Diagnostics 2025, 15(7), 914; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070914 - 2 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: The concept of mesopancreas is frequently discussed in the surgical literature as the neural pathway for metastatic spread in pancreatic head cancer. It generally refers to a retro-pancreatic plane that should be resected to reduce the incidence of regional metastases. However, this
[...] Read more.
Background: The concept of mesopancreas is frequently discussed in the surgical literature as the neural pathway for metastatic spread in pancreatic head cancer. It generally refers to a retro-pancreatic plane that should be resected to reduce the incidence of regional metastases. However, this concept remains poorly defined, both embryologically and anatomically. Our objective was to establish a clear embryological and anatomical definition of the mesopancreas, making anatomical data more applicable in surgical practice. Methods: We examined seven cadavers (5 males, 2 females, aged 62–71) with no medical or surgical history, preserved in 9% formalin at Carol Davila University’s Anatomy Department. Regional dissections were performed in successive planes, highlighting the celiac ganglia and the associated network of neural connections that comprise the mesopancreas. Results: Our study defines the “mesopancreas” as remnants of primordial mesenteries that coalesced into the Treitz fascia. We identified its functional components as nerve fibers linking the celiac ganglia and superior mesenteric plexus to the pancreas, along with vascular structures, lymphatics, and connective and adipose tissue. These components likely contribute to regional metastasis in pancreatic head cancer. While resection of the mesopancreas could help prevent metastasis, its complex anatomy and proximity to major vessels pose significant surgical challenges. Conclusions: Based on our findings, we propose a plausible definition for the term “mesopancreas”. It encompasses the structures that originated as part of the primordial mesenteries, which subsequently coalesced, resulting in the formation of the Treitz fascia. In essence, the mesopancreas is the functional content of a former mesentery.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Abdominal Diseases: Diagnosis, Treatment and Management)
►▼
Show Figures
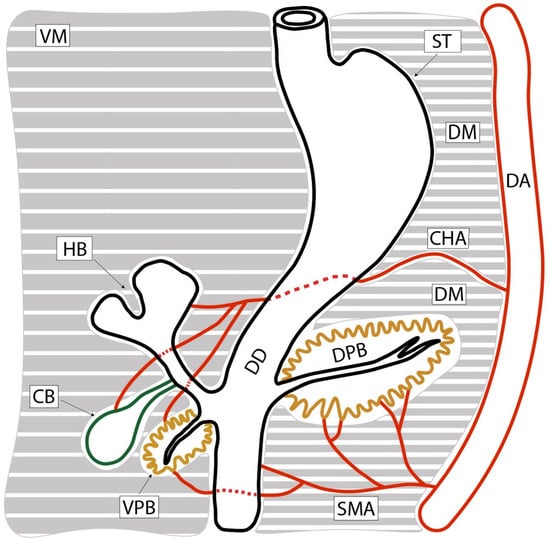
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Assessment of Immunoscore, MRI Tumor Regression Grade, and Neoadjuvant Rectal Score in Predicting Pathologic Response in Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer in the Averectal Study
by
Mustafa Natout, Ahmad Machmouchi, Hero Hussain, Laudy Chehade, Noura Abbas, Rim Turfa, Joseph Kattan, Sally Temraz, Ayman Tawil, Mousa Elkhaldi, Omar Jaber, Rula Amarin, Tala Alawabdeh, Maya Charafeddine, Monita Al Darazi and Ali Shamseddine
Diagnostics 2025, 15(7), 913; https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070913 - 2 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Predictive tools are needed to assess the response to treatment and guide treatment decisions for locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC). This study explores the value of combining the immunoscore (IS) and magnetic resonance imaging tumor regression grade (mrTRG) with pathologic and
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Predictive tools are needed to assess the response to treatment and guide treatment decisions for locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC). This study explores the value of combining the immunoscore (IS) and magnetic resonance imaging tumor regression grade (mrTRG) with pathologic and radiologic neoadjuvant rectal (NAR) scores in predicting pathologic complete response (pCRs). Methods: The scores were assessed for patients with LARC enrolled in the Averectal study (NCT03503630), who received five fractions of short-course radiotherapy, followed by six cycles of mFOLFOX-6 plus avelumab, and total mesorectal excision. The IS was calculated using the mean density percentiles of CD3- and CD8-positive T-cells on baseline biopsy samples. Baseline and post-treatment MRIs were reviewed to measure the mrTRG. NAR scores were calculated using the pre-treatment T stage and post-treatment pathologic and radiologic N and T stages. Results: Fifteen out of thirty-five patients whose data were available achieved pCR (42.8%), and seven out of fourteen patients with mrTRG = 1 (complete response) attained pCR. In patients with both a mrTRG = 1 and high IS, the pCR rate was 66.7% (6/9). All of the patients who achieved pCR had a low or intermediate pathologic NAR score with a significant correlation between pCR and pathologic NAR scores (p < 0.0001). Both pathologic and radiologic NAR scores were correlated with overall survival and disease-free survival. Conclusions: The IS can supplement the mrTRG to better predict TNT outcomes, along with the use of the NAR score. This combination could potentially help with patient selection for non-operative management and guide treatment strategies for those with different recurrence risks.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Diagnosis and Management of Colorectal Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Diagnostics Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
2 April 2025
MDPI INSIGHTS: The CEO's Letter #21 - Annual Report, Swiss Consortium, IWD, ICARS, Serbia
MDPI INSIGHTS: The CEO's Letter #21 - Annual Report, Swiss Consortium, IWD, ICARS, Serbia
1 April 2025
Meet us at the 11th Congress of the European Academy of Neurology, 21–24 June 2025, Helsinki, Finland
Meet us at the 11th Congress of the European Academy of Neurology, 21–24 June 2025, Helsinki, Finland

Topics
Topic in
Cancers, Current Oncology, Diagnostics, Diseases, Onco
Artificial Intelligence in Cancer Pathology and Prognosis
Topic Editors: Hamid Khayyam, Ali Hekmatnia, Rahele Kafieh, Ali JamaliDeadline: 1 May 2025
Topic in
Diagnostics, JCTO, JCM, JPM, Tomography
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) and OCT Angiography – Recent Advances
Topic Editors: Sumit Randhir Singh, Jay ChhablaniDeadline: 26 May 2025
Topic in
Biology, JCM, Diagnostics, Dentistry Journal
Assessment of Craniofacial Morphology: Traditional Methods and Innovative Approaches
Topic Editors: Nikolaos Gkantidis, Carlalberta VernaDeadline: 20 June 2025
Topic in
JCM, JPM, JVD, Diagnostics, Cancers
Diagnosis, Management, and Prognostic Assessment of Chronic Disease
Topic Editors: Xiude Fan, Enfa Zhao, Yang Xia, Shanshan Shao, Tatsunori Miyata, Dongxing XieDeadline: 5 July 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Diagnostics
Diagnosing, Treating, and Preventing Eye Diseases
Guest Editor: Ermete GiancipoliDeadline: 16 April 2025
Special Issue in
Diagnostics
Imaging in Oral Surgery: Advancing the Frontiers of Precision Diagnosis and Treatment Planning
Guest Editor: Anusha VaddiDeadline: 22 April 2025
Special Issue in
Diagnostics
Application of Neuroimaging Biomarkers in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Mental Diseases, 2nd Edition
Guest Editors: Deborah A. Yurgelun-Todd, Douglas Kondo, Nicolas A Nunez, Perry Franklin Renshaw, Dost ÖngürDeadline: 25 April 2025
Special Issue in
Diagnostics
Predictive and Prognostic Markers in Critically Ill Patients, 2nd Edition
Guest Editors: Silvia De Rosa, Sergio LassolaDeadline: 30 April 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Diagnostics
Clinical Guidelines/Expert Consensus on Diagnostics
Collection Editor: Zhongheng Zhang